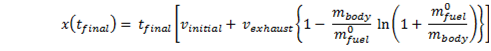|
Physics |
|
EOS |
|
Rocket Science |
|
Page 1 Momentum Derivation of the Rocket Equation Thrust
Page 2 Speed of the Rocket During the Burn
Page 3 Rocket Acceleration Position as a Function of Time
Page 4 Gravity
Page 5 Saturn V Data Stage 1 Calculation
Page 6 Saturn V Stage 2, Stage 3 Calculations
Page 7 Saturn V Photo Gallery
Page 8 Saturn V Photo Gallery
Page 9 Equation Review |
|
9 Equation Review |
|
Equation Review Variables mr(t) mass of the rocket vr(t) velocity of the rocket vexhaust velocity of the exhaust gas, relative to the rocket mgas(t) mass of the exhaust gas p total momentum R fuel burn rate T thrust m0fuel mass of full load of fuel mbody mass of the rocket body – excluding fuel mfinal rocket mass at the end of the burn tfinal duration of the burn a(t) rocket acceleration x(t) rocket displacement g acceleration due to gravity
The rocket equation in various forms
If there is no external force acting on the rocket, this is the form of the rocket equation ready to integrate
If there is an external force acting on the rocket, the expression for force goes on the left-hand side For gravity as a constant force:
For gravity as a variable force:
Relation between the time-rate-of-change-of-mass of the rocket and the exhaust gas
Fuel burn rate
Thrust
Speed of the rocket – no gravity
Rocket speed at the end of the burn
Rocket speed at some time t during the burn
Speed of the rocket if gravity can be considered a constant force
Mass relationships Rocket mass in terms of body mass and fuel mass
Initial mass of rocket – at ignition
If all of the fuel is burned, the mass of the rocket at the end of the burn is equal to the mass of the rocket body
Mass of the rocket as a function of time
Mass of the fuel as a function of time with a constant burn rate
Duration of the burn, if ignition occurs at t = 0
Acceleration – no gravity At some time t
At ignition
At the end of the burn
Acceleration if gravity is considered a constant force
Displacement of the rocket during the burn – no gravity
Displacement of the rocket at the end of the burn
Displacement if gravity is considered a constant force
Force of gravity acting on the rocket
Expression for g, in general, at the surface of a planet
|
|
webpages and Eos image copyright 2020 M Nealon |